Project background
The Rheinland-Pfalz region of Germany is the location of several geothermal power plants. Goethe-University Frankfurt installed a seismic array system to provide large-scale monitoring of seismicity in the region within the framework of a publicly-funded geothermal project.
Although array methodology for seismic monitoring has a long history, the project is focused on a new cost-effective array system for the detection of geothermally induced earthquakes. Array methods provide the ability to accurately locate seismic events across extensive regions, while significantly reducing the total number of required seismic stations.
Based on the experiences gained in earlier projects, existing array methods are being expanded for the purposes of seismic monitoring of geothermal plants.
The concentration of geothermal power plants in the Upper Rhine Graben provides a unique opportunity for simultaneous monitoring of several existing, as well as potential, future sites for geothermal power plants from one remote location with favourable noise conditions.
Additionally, the spatial proximity of the geothermal power plants near Landau and Insheim, separated by just 4 km, poses a special challenge for the assignment of the detected induced events to one of the two locations, requiring an innovative methodological approach. Specific array pattern functions are to be developed that can be used in a correlation approach to detect and identify induced earthquakes in the directional beam of the array.
Although array methodology for seismic monitoring has a long history, the project is focused on a new cost-effective array system for the detection of geothermally induced earthquakes. Array methods provide the ability to accurately locate seismic events across extensive regions, while significantly reducing the total number of required seismic stations.
Based on the experiences gained in earlier projects, existing array methods are being expanded for the purposes of seismic monitoring of geothermal plants.
The concentration of geothermal power plants in the Upper Rhine Graben provides a unique opportunity for simultaneous monitoring of several existing, as well as potential, future sites for geothermal power plants from one remote location with favourable noise conditions.
Additionally, the spatial proximity of the geothermal power plants near Landau and Insheim, separated by just 4 km, poses a special challenge for the assignment of the detected induced events to one of the two locations, requiring an innovative methodological approach. Specific array pattern functions are to be developed that can be used in a correlation approach to detect and identify induced earthquakes in the directional beam of the array.
Array design
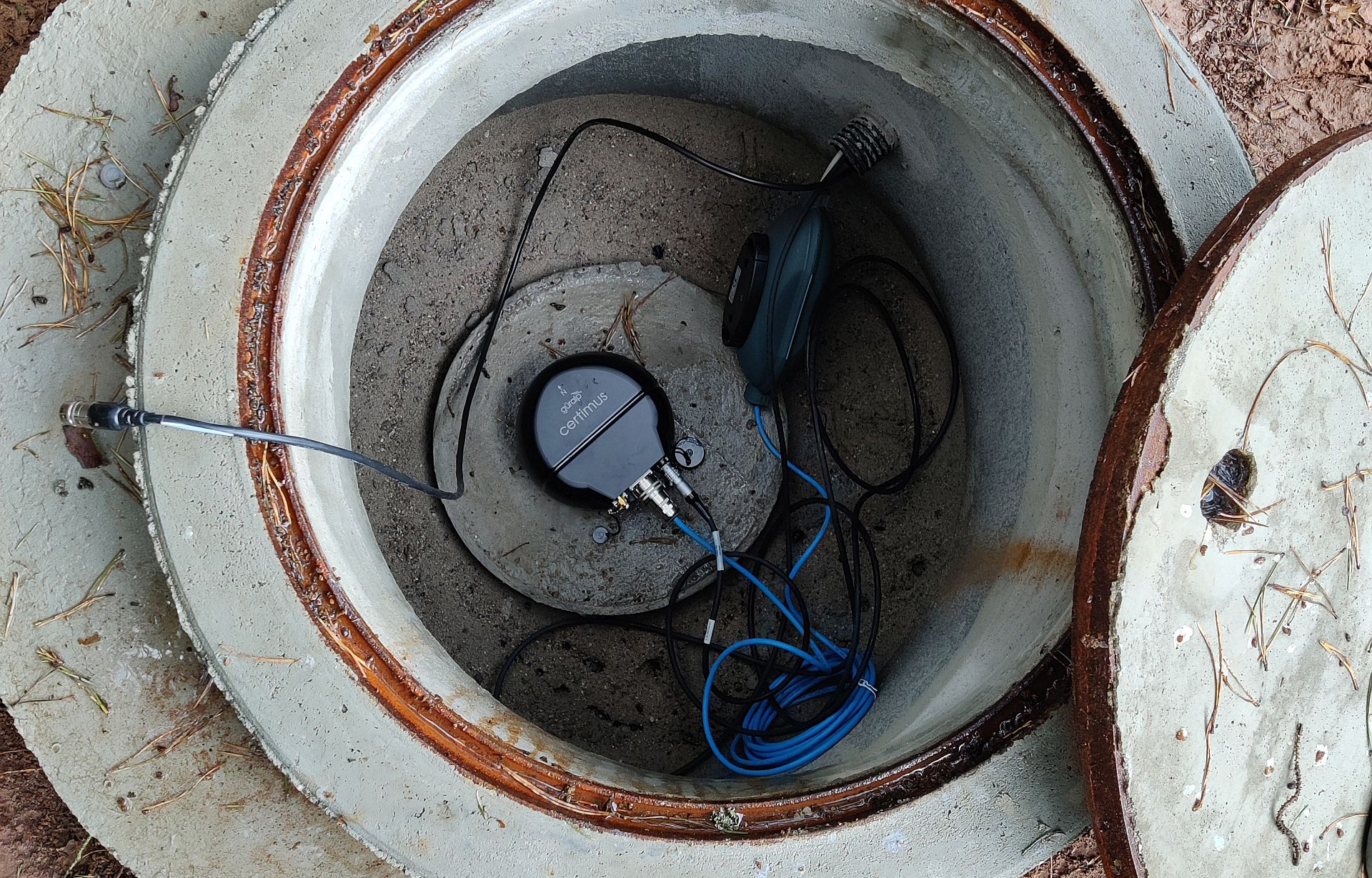
Nine Güralp Certimus seimic stations were deployed as part of a 10 station array. Each station, including LTE routers, is powered solely by solar panels utilising 2 x 160 Ah battery storage devices and 340 Wp solar panels, with no loss of performance, even during darker winter months.
Near real-time data transmission is achieved via cellular network, with a data sampling rate of 200 Hz, and data packages sent approximately every second. Data transmission works well, despite network coverage being rather sparse in the region.
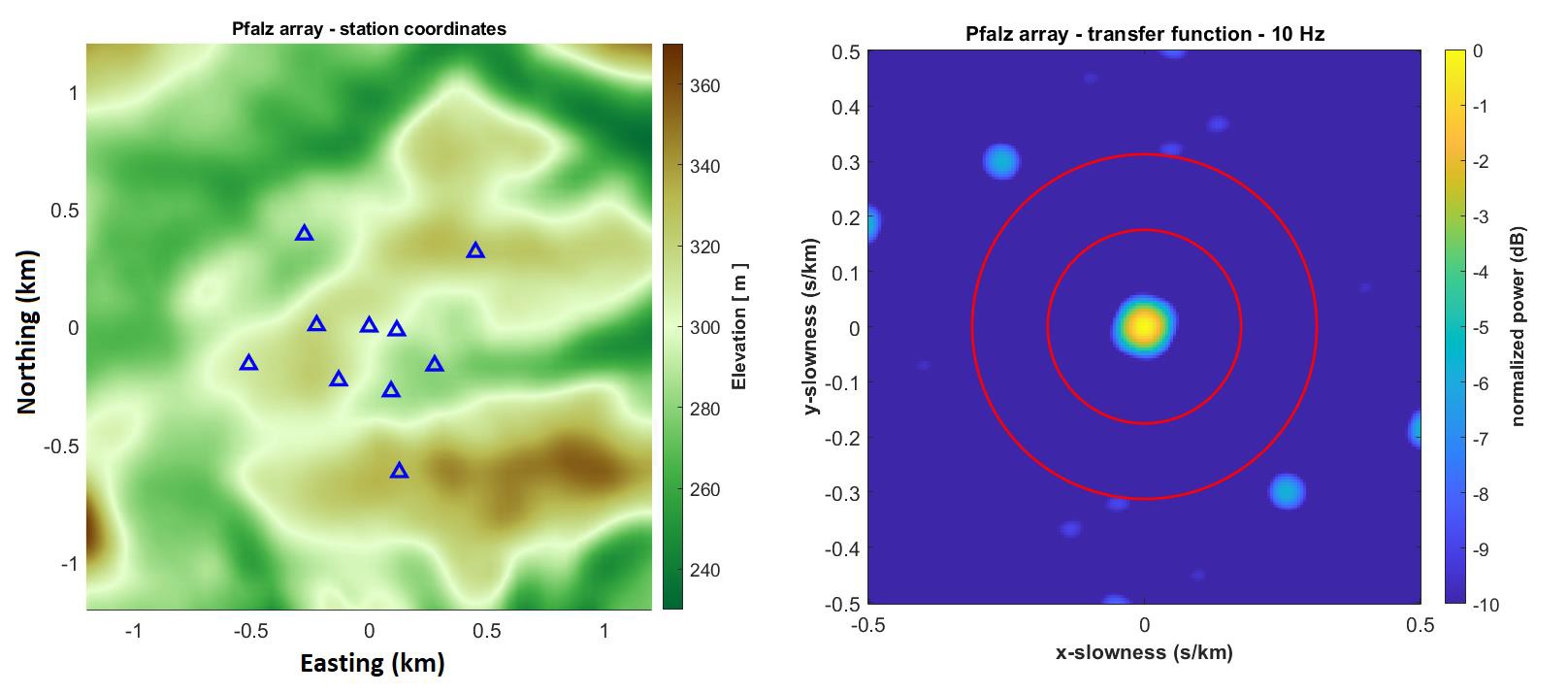
Figure 2 shows the station distribution and Figure 3 shows the array transfer function at a frequency of 10 Hz
Images provided by Dr. Philip Hering, Goethe-University Frankfurt
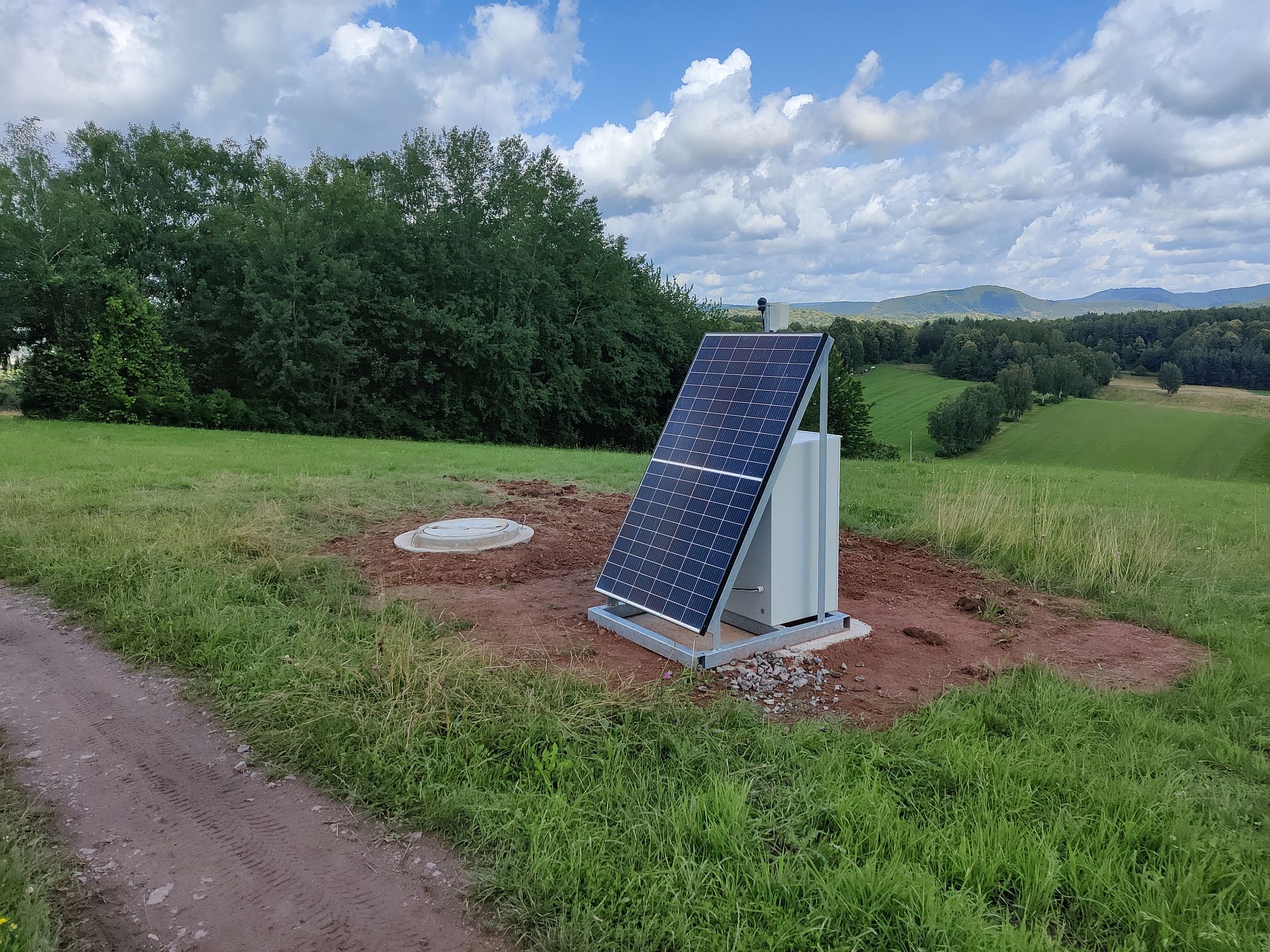

Figure 4 One of the completed array stations
Image provided by Dr. Philip Hering, Goethe-University Frankfurt
The Güralp Solution
Certimus
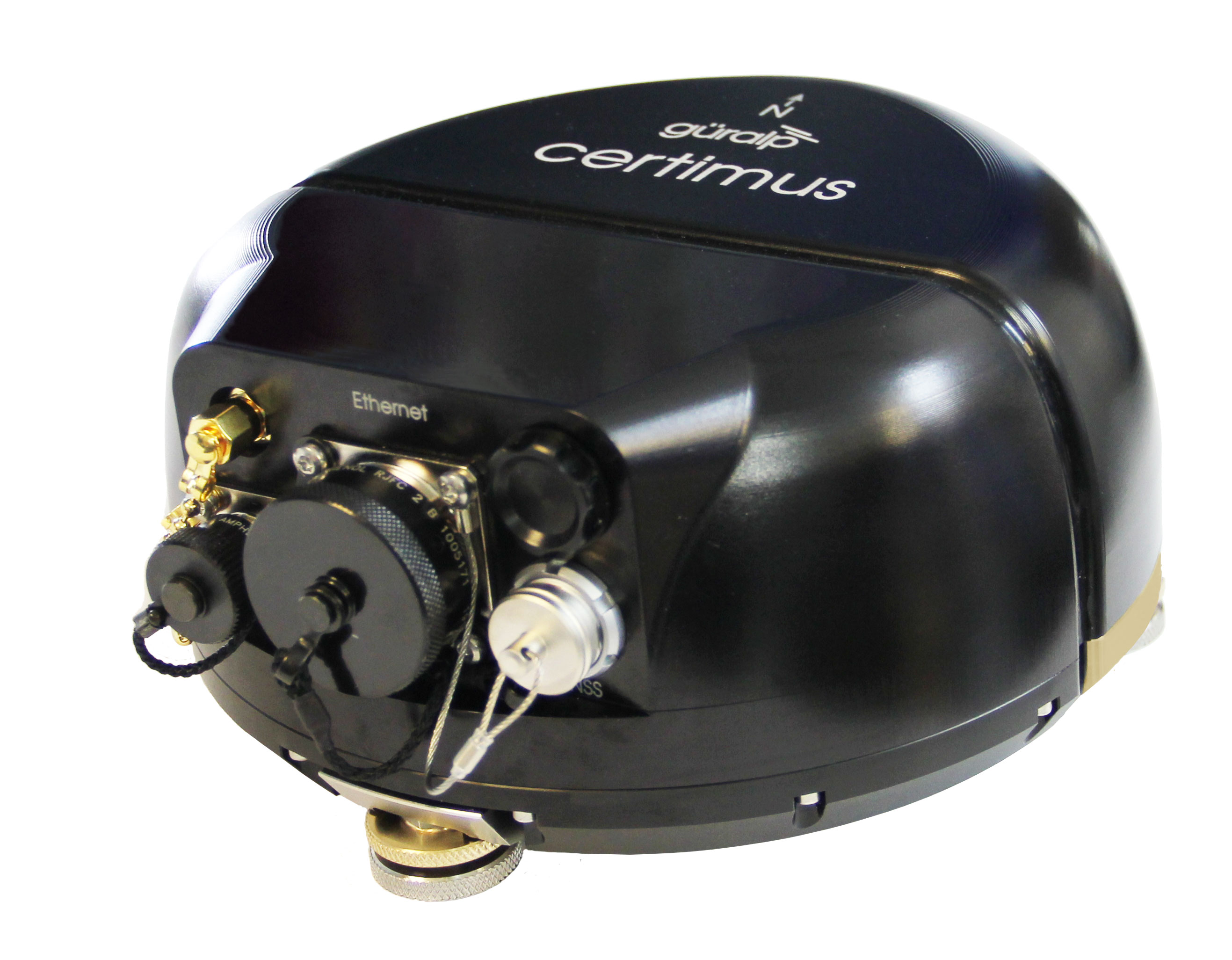
Certimus is an all-in-one portable, digital, broadband triaxial seismometer with state-of-the-art communication capabilities suitable for direct burial, surface and vault deployment. Certimus can operate at angles up to 90° from level for simplified installations.
With a wide frequency response of 120 s - 100 Hz, the low-power Certimus also benefits from a remotely adjustable long-period corner. The 1 and 10 second modes can be adjusted pre- or post-deployment and significantly reduce the settling time of the sensor. Power over Ethernet (POE) and Wi-Fi allow for plug-and-play deployments.
With a wide frequency response of 120 s - 100 Hz, the low-power Certimus also benefits from a remotely adjustable long-period corner. The 1 and 10 second modes can be adjusted pre- or post-deployment and significantly reduce the settling time of the sensor. Power over Ethernet (POE) and Wi-Fi allow for plug-and-play deployments.
Outcome
At this stage the array is collecting data to establish a solid data base for classification algorithms. If successful, the array might integrated with the existing conventional seismic networks operated by the regional authorities and the geothermal companies that provide the traffic light warning system for the geothermal plants.
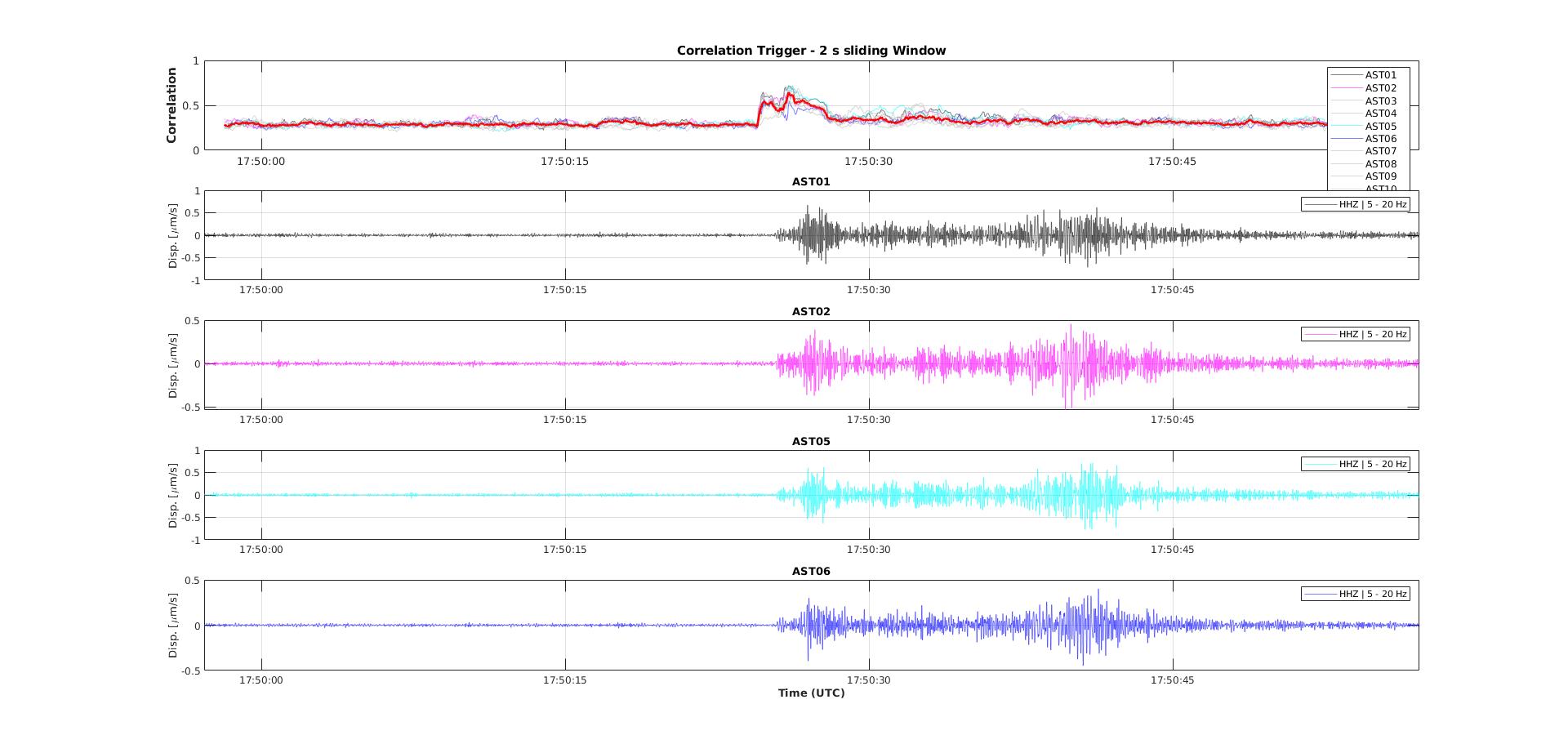
The waveforms below are of a tectonic earthquake that occurred 112 km from the array.
The waveforms below are of a tectonic earthquake that occurred 112 km from the array.
It is hoped that independent monitoring of seismic activity in geothermal plants, plus increased accessibility of relevant information (via the Internet), will contribute to improving public acceptance of geothermal energy projects.
Figure 5: Waveforms of a tectonic EQ (M 1.4) that occurred 112 km distance from the array. The image shows the Z-component at 4 Array stations.
Image provided by Dr. Philip Hering, Goethe-University Frankfurt
"The signal to noise ratio is impressively high considering the distance to the array and the relatively small magnitude."
Dr. Philip Hering
Institute for Geosciences, Geophysics, Goethe-University Frankfurt
Dr. Philip Hering
Institute for Geosciences, Geophysics, Goethe-University Frankfurt
References
(1) https://www.enargus.de/pub/bscw.cgi/?op=enargus.eps2&q=seiger&v=10&id=1213503
(2) Dr. Philip Hering, AG Seismology, Institute for Geosciences, Goethe-University Frankfurt am Main
Figures 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6 provided by Dr. Philip Hering, Goethe-University Frankfurt.
(2) Dr. Philip Hering, AG Seismology, Institute for Geosciences, Goethe-University Frankfurt am Main
Figures 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6 provided by Dr. Philip Hering, Goethe-University Frankfurt.