
Chapter 3. Configuring the NAM (server)
3.1 Connections
The NAM should be connected to a suitable power supply and network as normal.
A CMG-ELP-0047 GPS receiver should be connected to either Port A or Port B of the NAM, using adapter cable CAS-ELP-0014 (see section 5 for cable details).
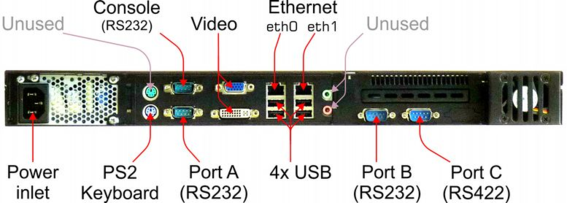
The adapter cable has:
a DE9 female connector for attachment to Port A or Port B of the NAM;
a ten-pin bayonet connector for attachment to the GPS receiver; and
an integrated power supply adapter with an IEC inlet for mains (line) power.
This cable provides power for the GPS receiver and connects the receiver's outputs (NMEA and PPS) to the NAM.
3.2 NTP configuration
In the web interface of the NAM, visit
Home → Configuration → Data handling → Timing
The following screen is displayed:
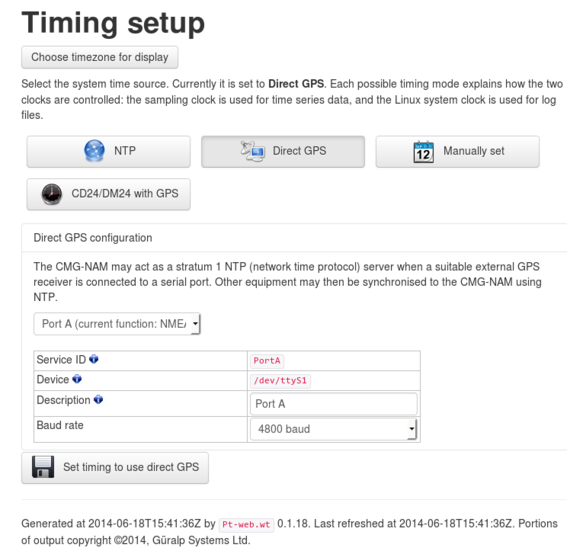
The first line beneath the  button indicates the current timing mode. If this is not Direct GPS, click the
button indicates the current timing mode. If this is not Direct GPS, click the  button to select this mode.
button to select this mode.
From the first drop-down menu, select the correct serial port – Port A or Port B – ignoring the displayed current function.
Check that the other parameters are as shown in the screen-shot above and then click  . The chosen serial port will be reconfigured.
. The chosen serial port will be reconfigured.
3.3 Diagnostics
Note: Even under ideal conditions, it can take up to thirty minutes for the NTP subsystem to synchronise to GPS.
3.3.1 The status display
The main status display has a tab for NTP status:
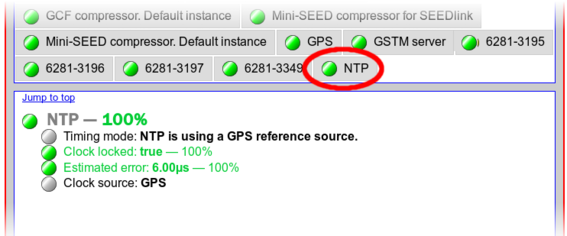
The status information is refreshed every five seconds (although you need to manually refresh to see any updates). It confirms the timing mode and indicates whether the clock is locked or not, along with the estimated error.
A similar tab displays the GPS status:
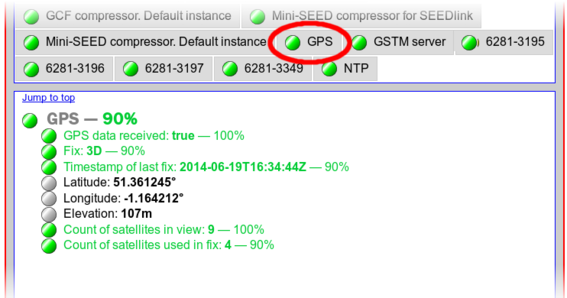
This confirms that GPS data are being received and displays some summary information decoded from the NMEA output from the GPS receiver.
3.3.2 Command-line tools
3.3.2.1 ntpdc
The standard ntpdc command displays the NTP daemon's status:
NAM001 ~ # ntpdc -p
remote local st poll reach delay offset disp
============================================================
*SHM(1) 127.0.0.1 0 16 377 0.00000 0.000002 0.01529
NAM001 ~ #
The GPS receiver appears as SHM(1). The preceding asterisk ('*') indicates that it is being used by NTP as its primary synchronisation source. For more information, please see the ntpdc manual at http://man.cx/ntpdc(1).
3.3.2.2 gpsmon
The standard Linux gpsmon command is available for monitoring the status of the GPS receiver daemon (gpsd):
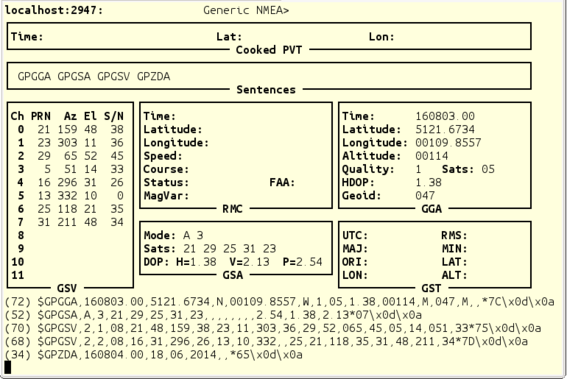
The display shows the decoded output of selected NMEA sentences (of which, GSV, GGA and GSA are the most relevant) and a real-time, scrolling display of the incoming NMEA from the receiver. Type  +
+ to terminate the display and exit the command.
to terminate the display and exit the command.
For more details, please see the gpsmon manual at http://man.cx/gpsmon(1).